
- Created2019.11.26
Ecofriendly Nano-fabrication Achieved with Biodegradable Chitosan Nanoparicles
-KIMM uses chitosan to fabricate self-cleaning antireflective glass-
-Biodegradable material paves way for nanostructuring with minimal environmental risks-
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM, President Chun Hong Park) succeeded in creating glass with self-cleaning and antireflective functions through the biodegradable chitosan nanoparticle coating. This is the first use of a biodegradable material in nanosphere lithography. The results of the study can be utilized to prevent the use of synthetic polymer nanoparticles in nano-fabrication, a kind of microplastic waste, which have been associated with toxicity issues.
Dr. Hyuneui Lim and Dr. Seung-Chul Park of the Department of Nature-Inspired Nano Convergence Systems under the Nano-Convergence Mechanical Systems Research Division used chitosan, obtained from crab shells, to develop an ecofriendly nanoparticles coating process, and published the results in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces* . (Oct. 30)
* Title of paper: Synthesis of Surface-Reinforced Biodegradable Chitosan Nanoparticles and Their Application in Nanostructured Antireflective and Self-Cleaning SurfacesThe team used biodegradable chitosan nanoparticles instead of polystyrene nanoparticles in the nanostructuring of antireflective, self-cleaning glass surfaces. The main advantage of the proposed process is that the use of ecofriendly material eliminates the microplastic waste, which occurs in nanostructuring processes.
With the growing interest in environmental issues, extensive research has been conducted to adopt ecofriendly approaches in nano-fabrication processes. However, it has been difficult to use biodegradable materials due to their weak intrinsic properties.
The team strengthened the physical properties of biodegradable chitosan nanoparticles through surface treatment and used it instead of polystyrene, which is a more commonly employed material in nanoparticle coating.
While chitosan particles have been used in food or drug delivery, this is the first approach of chitosan in nanosphere lithography. The results are expected to lead to diverse applications in processes involving polymer nanoparticles.
To date, the cheap, spherical polystyrene polymers have been used to make nanostructures on surfaces. This process produces large amounts of waste containing plastic nanoparticles, and has been a significant environmental concern.
Hyuneui Lim, head of the Department of Nature-Inspired Nano Convergence Systems, said, “The significance of this study lies in being the world’s first ecofriendly nanosphere lithography that successfully reduces the use of nanoplastic particles. We expect it to have various applications in processes requiring the use of polymer nanoparticles.
The study received funding from the Convergence Research Program of the National Research Council of Science and Technology as a “preliminary study on Teflonreplacing high-temperature resistant superhydrophobic surface design and process technology”, and from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy for the “development of self-cleaning high-value-added color glass for solar modules in urban buildings.”
Attachments (Large-size photos will be sent separately): - Attachment 1: Comparison of Ecofriendly Nano-fabrication Using Chitosan and General Nano-fabrication Using Polystyrene (Picture)
- Attachment 2: Biodegradability of Chitosan Nanoparticles According to Time (Photo)
- Attachment 3: Self-cleaning Test of Nanoglass Made from Biodegradable Chitosan Nano-particles Based Fabrication (Photos)
- Attachment 4: Participating Researchers (Photo)
- Attachment 1: Comparison of Ecofriendly Nano-fabrication Using Chitosan and General Nano-fabrication Using Polystyrene (Picture)
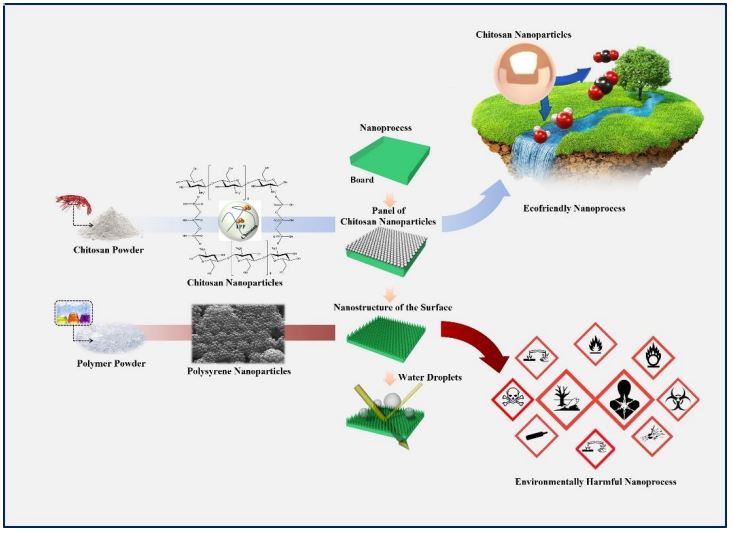
Description: Nano-fabrication schematic for the self-cleaning antireflective glass by ecofriendly nano-fabrication using chitosan and general nano-fabrication using synthetic polymer nanoparticle
- Attachment 2: Biodegradability of Chitosan Nanoparticles According to Time (Photo)
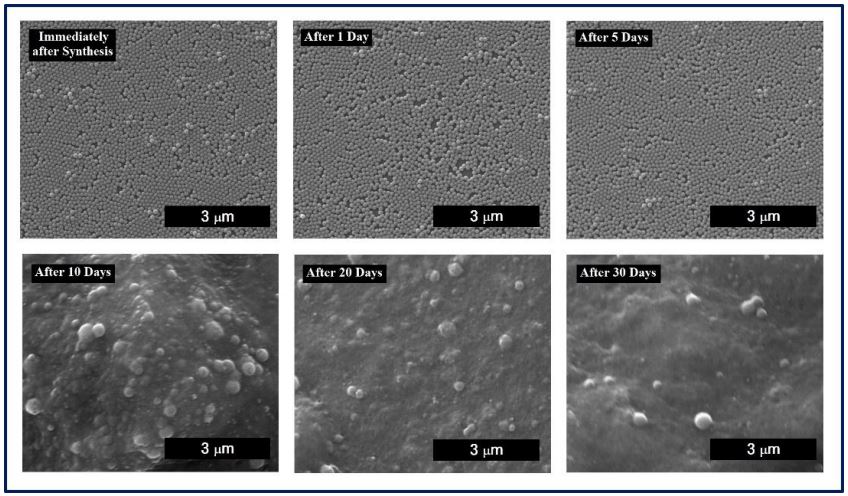
Description: SEM images of changes in chitosan nanoparticles over time when stored at room temperature. Chitosan nanoparticles are decomposed after 30 days.
- Attachment 3: Self-cleaning Test of NanoglassMade from Biodegradable Chitosan Nano-particles Based Fabrication(Photos).

Description: Comparison of water flow of typical glass and self-cleaning glass made from chitosan nanoparticles based fabrication. When water is dropped, water droplets show at a contact angle of 23 degrees on typical glass, but roll off the self-cleaning glass with a larger contact angle of 152 degrees.

-Attachment 4: Participating Researchers(Photo)

Description: Corresponding author Dr. Hyuneui Lim and first author Dr. Seung-Chul Park



