Generating a multi-focus laser beam inside the transparent
substrate to enable cutting a substrate thicker than the depth of
focus or drilling of micro holes with high aspect ratio.
Client / Market
- Laser machining system manufacturer, display manufacturer, companies using
precise cutting or micro machining of glass/sapphire/wafer
Necessity of this Technology
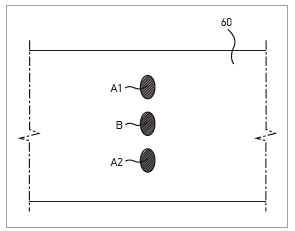
- Technology for high speed cutting a transparent substrate thicker than the depth of
the single focus laser beam with one scan is needed.
- To cut a transparent substrate thicker than the depth of focus of the laser beam,
a focusing lens with lower magnification needs to be used to increase the depth of
focus, or laser beam has to be scanned multiple times with readjusted focus point
to cover the thickness of the substrate.
- When using a focusing lens with low magnification, the cutting width is broadened,
and machining becomes less precise.
- When processing multiple times by adjusting the focus along the substrate, the
overall cutting speed becomes slow, which leads to decreased productivity.
- A multi-beam with adjustable number of focus and spacing between the focal
points depending on the substrate thickness needs to be created.
Technical Differentiation
- By splitting the laser beam into two or more beams and adjusting the spacing
between the focal points to efficiently align them to suit the thickness of the object,
and then cut or bore with the multi-focus beam, the process time is shortened
as the process speed is faster compared to a laser machining system that uses a
single focus.
- If a high-power laser is used as single-focus beam, the optimal output for
machining is lower than the maximum laser output that the laser output needs to
be lowered, which means the laser’s capability is not exercised 100%. However, by
machining with multi-beam, the laser intensity is maintained at its optimal output
and the laser’s maximum capacity is utilized.
- Compared to existing beam splitter (divided into interference method and
birefringent lens splitting method), the multi-focus device using diffractive optical
element (DOE) splitter has following benefits.
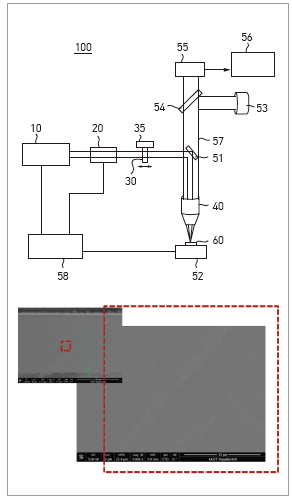
- By using the DOE splitter as the beam splitter, all beams propagate same optical path
until being split by the object lens. The optical configuration becomes simple, and beam
alignment is easy.
- Maintaining the polarization direction, which is not possible with polarization splitting
- Possible to adjust the number of focal points and spacing: By adjusting the DOE optical
system, multiple beams set according to the number assigned are aligned, and the
spacing between the beam inside the glass is easy-favorable for cutting and micro
machining of glass of various thickness.
Excellence of Technology
- The purpose of this technology is to adjust the number and distribution of laser
beams according to the substrate thickness for cutting, drilling, or bonding
transparent materials and achieve optimal energy distribution of the beam for
machining inside the substrate.
- Optical configuration is simple as DOE acts as a laser beam splitter and a lens.
- Split beams propagate along the same optical path, and are precisely split at the
object lens focus point to form multiple focal points inside the object along the
thickness of the substrate.
- The number of beams can be assigned as desired to be applied on thin or thick
glass plates.
Current Intellectual Property Right Status
PATENT
- Substrate Cutting Method Using Fresnel Zone Plate(KR1015826320000)
KNOW-HOW
- Ultrashort pulsed laser-based micromachining technology of brittle materials
(glass, sapphire, quartz, silicon wafer)
|






