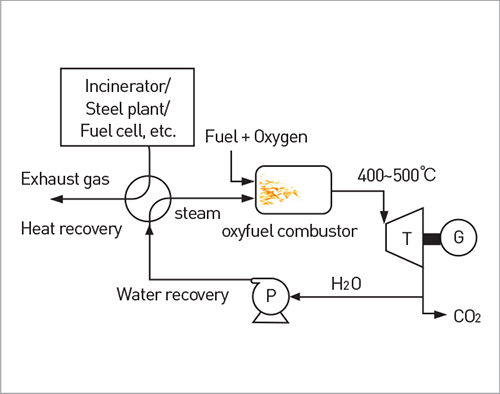
Combustion and generation system technology that links waste heat or waste steam generated from large thermal facilities like incinerators and steel plants with oxyfuel combustion technology to acquire electricity while also collecting CO2
Client / Market
- Large capacity heat discharge facilities including heating furnace, incinerator, steel plant, fuel cell system
Necessity of this Technology
- The technology to reduce CO2 emission, the main cause of global warming and climate change, is a globally important technology. Various technologies such as efficiency improvement, waste heat recovery, combination with new and renewable energy, CO2 capture and storage (CCS) technology are being developed.
- Existing technologies that recover waste heat from facilities to generate power include organic Rankine cycle (ORC), thermoelectric generation system, but their efficiency is low, and the power output is low considering the initial investment that it is economically disadvantageous.
- CO2 capturing technology that can be applied for power generation system can be classified into pre-combustion, post-combustion, and oxyfuel combustion. There is an issue of the efficiency decreasing by 10% due to oxygen producing electricity, and because of this issue, economic feasibility cannot be secured.
- A countermeasure is needed such as efficiency improvement of the components to overcome efficiency decrease and a new concept cycle, etc.
- Technologies such as Pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) combustion, high-efficiency CO2 capturing generation system are needed.
Technical Differentiation
- To realize high-efficiency system, this “Waste heat recovery type oxyfuel combustion generation system technology” utilize energy from incinerators and steel plants that goes into waste to produce steam and combine the steam with oxyfuel combustion gas to supply to the turbine to generate power.
- By using waste heat or steam, the efficiency decrease issue of previous CO2 capture technology can be overcome.
- Entire CO2 contained in supplied fuel can be captured, and by applying unused steam in the oxyfuel combustion generation system, efficiency decrease from oxygen generation is minimized, and economic feasibility can be secured.
- For the same investment, greater power can be generated so its economic feasibility can be secured. Captured CO2 can be recycled (for greenhouse cultivation)
- A large-scale empirical study on CO2 capturing generation technology is being conducted internationally (Clean Energy System of the USA, etc.), but there is no study that considers efficiency decease.
- Proposed system is a new concept cycle designed to minimize efficiency decrease.
- It is an original technology for an independent Pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) combustor design using the lean burn technology of gas turbine.
Excellence of Technology
- The technology can be largely divided into “pure oxygen combustor technology” and “system integration and control technology”.
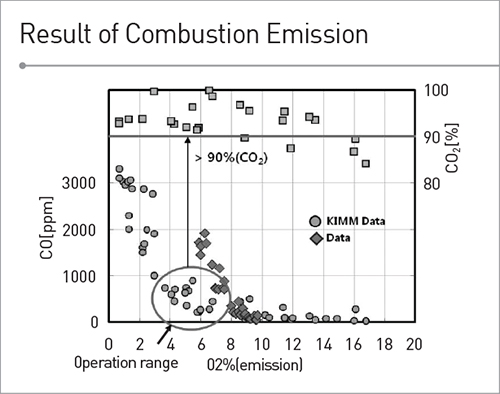
- Key component is the “oxyfuel combustor” that supplies steam while stably maintaining the flame and realize perfect combustion. (CO emission concentration that represents imperfect combustion is very low.)
- Combustor emission property was outstanding compared to that of advanced companies.
- A 100 kW-level pilot plant was established in the experiment building at KIMM, and empirical operation was successfully done. (power generation of 80 kW, CO2 concentration of 93%)
- 18 SCI papers (system analysis/oxyfuel combustion/turbine development, etc.), 10 papers in Korean, and 40 domestic/international academic presentations
- Press coverage by YTN (Dec. 7, 2011), Yonhap News (Nov. 30, 2010), The Korea Economic Daily, The Korea Electric Power News, Daejeon Ilbo
- A project manager over 30 years of research experience (clean combustion technology) and 10 doctorate researchers participated in the study.
Current Intellectual Property Right Status
PATENT
- Fuel Cell-Linked Power Generation Plant Using Pure Oxygen Combustion and a Control Method Thereof (KR1067509)
- Method and Combustion Apparatus (KR0395646, KR0395647, KR0397210)
- Oxyfuel Burner with Flue Gas Recirculation (KR0590845)
- Low NOx Oxyfuel Burner with High Speed Injection (KR0657864)
- Combustion System Including Exhaust Gas Recirculation Unit Using Ejector (KR0707520
- Thermal Power Plant Having Pure Oxygen Combustor (KR0814940, PCT/kr2008/002600, CNZL 2008 8 0000374.6, EP08753396.4)
- Thermal Power Plant Having Pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) Combustor and Using Waste Steam (KR0779609)
- Overheating Preventing Gas Turbine System (KR0862374)
- Gas Turbine System (KR0890823)
- Gas Turbine System for Low NOx emission (KR0890824)
- Fuel Cell-Linked Power Generation Plant Using Pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) Combustion (KR0817898)
- Turbine Blade and Turbine Using It (KR0916354)
KNOW-HOW
- Pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) combustion gas turbine generation system analysis technology (process modeling, economic feasibility assessment, eco-friendliness assessment technique)
- High pressure pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) combustor design technology
- Pure Oxygen (Oxyfuel) combustion gas turbine generation system operation control technology
|






